This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.

Smart Technologies in Urban Agriculture
Smart technologies are revolutionizing urban agriculture by transforming traditional farming practices into highly efficient, sustainable, and data-driven systems. By integrating innovative tools and digital solutions, city-based agriculture is becoming more productive and environmentally friendly, addressing the challenges posed by urban density and limited space. The adoption of smart technologies in urban farms is fostering increased yields, resource efficiency, and streamlined operations, paving the way for cities to become more self-sufficient in food production while reducing their environmental footprint. As urban populations continue to grow, these technologies play a crucial role in meeting the demand for fresh, nutritious, and locally produced food.
Precision Farming and Data Analytics
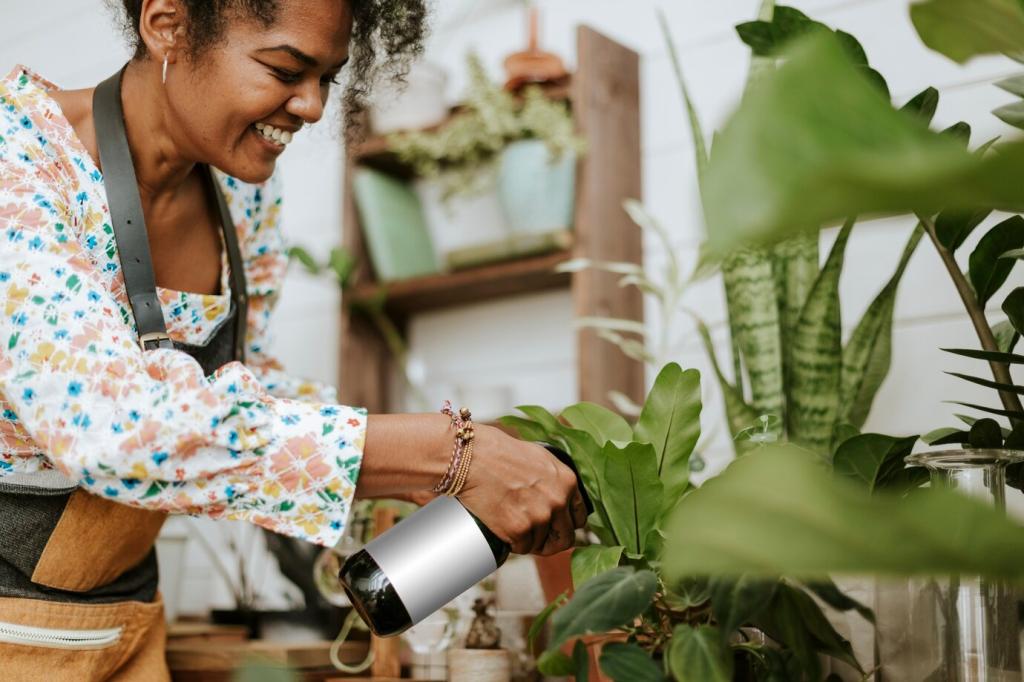


Automated Irrigation Systems
Robotic Planting and Harvesting
Monitoring and Maintenance Drones
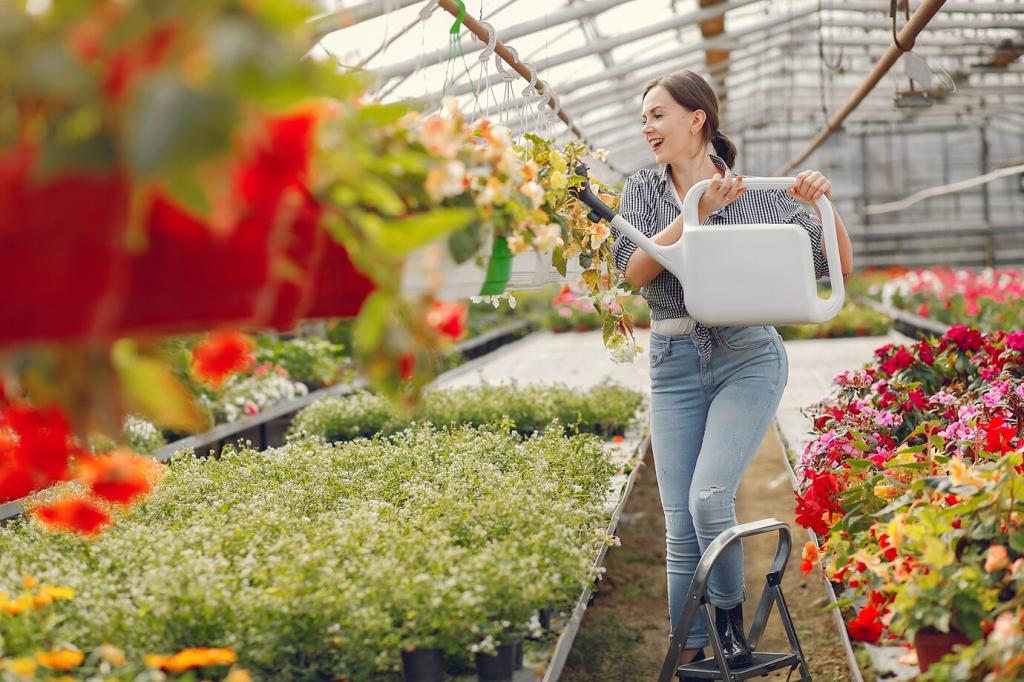

Smart Water Management

Energy-Efficient LED Lighting